Abstract
While Blockchain has become a widely discussed and hailed distributed ledger technology across the banking world, its impact on the insurance space is yet to be witnessed. From product innovation, effective fraud detection, to reduced operational costs, Blockchain has the potential to address some of the key challenges plaguing the insurance industry today. Given that implementing Blockchain is a long-term engagement that requires consistent collaboration between market participants and technology leaders, it is essential to carefully assess the technology implications and define network and regulatory conditions. That said, the time for insurers to invest time and resources in Blockchain—as individual players and as an industry—is now.
Time to Evaluate Blockchain for the Insurance Space!
Blockchain is a relatively new technology for the insurance industry, and is currently going through the litmus test phase. Many major insurers are investing in Blockchain, for the fear of competition moving ahead of them.
Traditionally, the insurance sector has been slow to adopt new technology and is often the last financial sector to incorporate any technological evolution, and Blockchain is no exception. However, it is important to note that the concept of Blockchain is being looked at as one of those rare innovations, which has the potential to disrupt the insurance industry much ahead of the trend.
The insurance industry is all about managing financial risks and includes a high volume of financial transactions on a day-to-day basis. This makes the industry vulnerable to a potentially large number of intrusions, attacks, and fraudulent transactions. The insurance space is also highly complex with composite contracts between multiple stakeholders that require a large processing potential. In this thought paper, we will review some of the current challenges in the insurance space, and analyze if Blockchain can provide the much-needed solutions.
Implications for the Insurance Industry
Blockchain is being assessed from multiple perspectives to find appropriate use cases and the insurance industry is no different. In Insurance, Blockchain can be applied at a more fundamental level because it automates the basics of insurance carrier value proposition: TRUST.
There are many areas across the insurance space where Blockchain can add value and help resolve challenges. Some of these include:
- High volume of digital transactions involving third-party gateways
- Identity thefts and frauds
- Delays in claims processing due to unreliable processes
- Managing multi-party insurance (TPAs, Re-insurers etc.)
- Reducing administrative cost by automating key processes
Problem Statement: Use Case of the Insurance Industry
To simplify the applications of Blockchain, let us take a typical use case from insurance.
John buys insurance for his specialized high value truck from insurance company X. His truck is a specialized one, and thus has a very high insurance value. In order to decentralize the risks and showcase sound financial judgement, company X extends the insurance to re-insurer company Y, which is part of an insurance consortium.
Let us assume that John has a quarterly billing plan and pays his premium every three months. In such a scenario, John has distributed his premium between multiple entities to be cleared at regular intervals.
Now, tracking John’s payment until the last dollar can pose a transactional challenge that many insurers deal with across the industry on a daily basis. To add to the complexity, if there is any claim from John, it involves reverse transactions, which include all insurers and re-insurers. Some of the pain areas in such a scenario are:
- Possible financial loss during digital transactions
- Possible fraudulent or duplicate claims (John may have insured the same truck with another insurer and may have received a claim from them)
- Complex and unreliable reconciliation processes
- The above scenario is a typical challenge that the insurance industry faces, and it possesses transactional and contractual complexity.
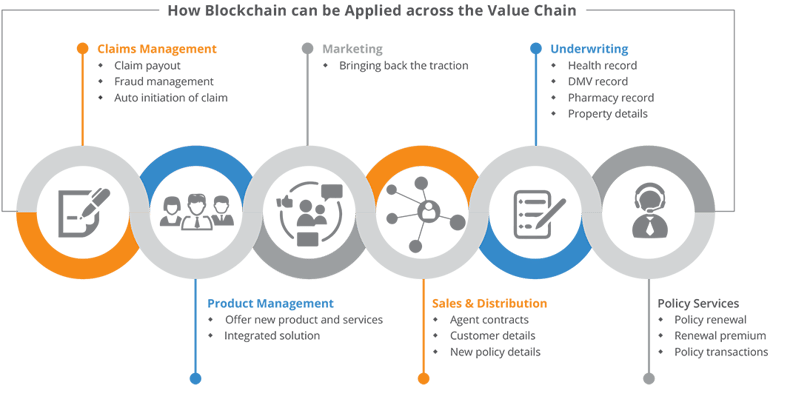
Figure 1
Can Blockchain Help?
The aforementioned problem is an ideal application opportunity for Blockchain implementation, especially if all the insurers in question are part of a private consortium. Blockchain can provide significant benefits to the consortium and all of its participants, including the insured customers like John. Blockchain can address the fundamental challenge of managing and tracking the distributed digital transactions of the problem scenario, as they will be extremely secure, manageable, and high-speed transactions.
Blockchain has the potential to provide a well-structured mechanism of managing and maintaining transactions, relevant public distributed ledgers, while minimizing operational costs from third parties. It will also help customer retention by optimizing processes.
An important aspect of Blockchain is the way it is implemented with the digital ledger. In the Banking sector, Blockchain technology along with Bitcoins has been extremely disruptive, being considered alternative currency. Not all countries have started accepting such digital currency, but the acceptance has seen a positive trend so far.
In the insurance industry, based on the implementation scope, Blockchain may see a high demand too. We believe that Blockchain can contribute immensely, if the scope and implementation are captured and defined appropriately. Blockchain requires investment and expertise, and its success demands a change in business thought leadership.
Does this mean Blockchain can solve most of the challenges faced by insurers? No. We recommend that it should be viewed as a specific solution, and one needs to analyze if such a solution fits in as a resolution of any given problem statement.
Some of the areas where Blockchain is already causing significant disruption in insurance by providing appropriate solutions to historic challenges are:
- Decentralized consortiums in insurance, re-insurance, and retrocession (B2C, B2B)
- Insurance consortiums (including underwriting, billing, and handling of claims fraud)
- Underwriting for claim avoidance including automation in claims settlement and disbursement (use of IoT devices in a Blockchain environment)
- Customer experience
- Fraud detection and pricing (Peer-to-Peer insurance, as a relatively new concept has already disrupted the industry)
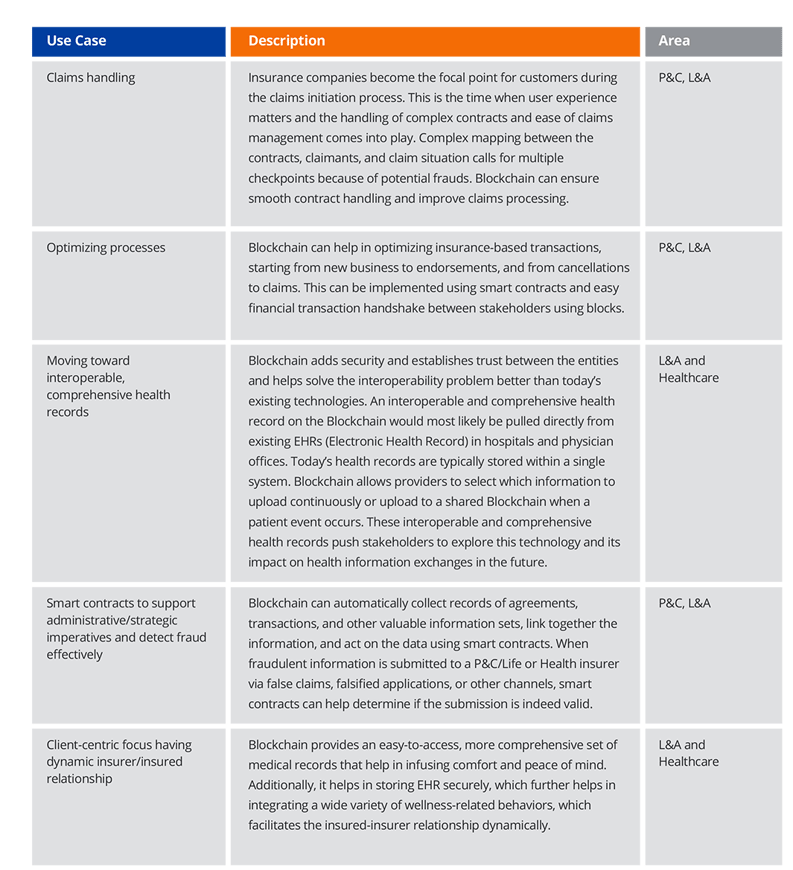
Figure 2: More Insurance Use Cases for Blockchain
Are there Limitations to Blockchain?
Blockchain can be implemented under certain conditions only, i.e. multiple parties should be involved and the data on which the results are based should be accurate and unchangeable over time. What happens in a situation where parties are limited, data is not reliable, and there is already a trusted intermediary in place?
In such situations, Blockchain has limitations in terms of the following 3S:
- Scalability because of continuously growing data that needs ongoing replications and validations
- Security because of evolving, newer threats that have not been experienced, understood, or mitigated yet
- Standardization because Blockchain is a new area, it lacks standardization and investment decisions

Figure 3: Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain Technology*
How Blockchain Can Alter the Insurance Landscape
Blockchain, in the insurance space, is still in its initial phase. The industry is yet to see a full-blown Blockchain implementation in production environments.
Some of the trends we expect to see with Blockchain in insurance space are:
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) insurance with Blockchain will create a potentially autonomous, self-regulated business model. P2P insurance model follows a similar business principle as Blockchain, i.e. presence of no single controlling authority and high transparency. This will be adapted more and we can expect large players to start participating in it.
- More and more large players, especially re-insurance and consortiums to invest on Blockchain, especially for transactions, claims
- Smart contracts and digital assets to become a reality
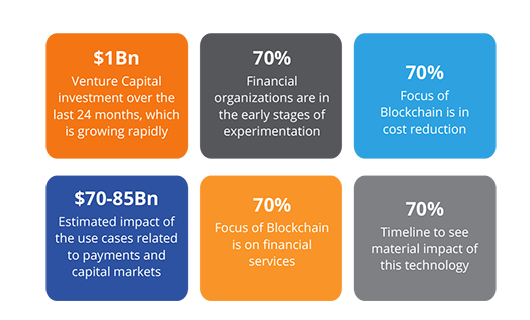
Figure 4: Blockchain in the Insurance Landscape**
Recommended Approach for Insurers
- Review existing collaborations/consortiums in business and identify critical challenges. This will help insurers analyze if Blockchain can help in collaborative environments
- Blockchain is a great boom for any insurer participating in P2P insurance domain. Understanding the pros and cons of Blockchain on P2P insurance space before investing will be vital.
- Take time to understand the advantages of implementing smart contracts in business. This will help insurers to be ready for the next big change with Blockchain.
- Deep dive into the claims process to understand customer’s pain points. This is very important and can bring in positive disruption.
- Include Blockchain as a shared mechanism for insurer carriers (via inter-company claims) to manage the subrogation process quickly, efficiently (in terms of admin cost), and diligently, leaving no scope for fraud.
- Invest in understanding the limitations of Blockchain and related technologies. This will help insurers (CTOs) to ensure they do not go by any hype, and are able to take informed decisions.
- Blockchain can enable trust between peers to help increase transparency in micro-insurance. It helps overcome any geographic and collaborative limitations
- Regulatory and compliance requirements have been driving the insurance industry. Insurers need to understand that Blockchain works in a completely different theory, i.e. Blockchain is transparent and not regulated and can potentially reduce centralized controls.
- Blockchain is a great solution for re-insurers. Since re-insurers are already part of collaborative environments or consortiums, their ability to utilize Blockchain should enhance their operational efficiency.
About the Author
Sriram Natarajan is a Solution Architect with over 17 years of leadership experience spanning delivery, program management, technology solutions, and enterprise architecture in insurance. His vast domain and technical expertise has been instrumental in the successful delivery of various programs he has been associated with. Sriram has done Masters in Computer Application from Tamil Nadu University, in addition to a Bachelor’s degree in Mathematics from Delhi University
Vikram Singh works as Practice Lead for insurance. He is a Business SME, bringing over 20 years of rich exposure in successfully executing and designing insurance solutions for various clients across the globe. His vast insurance domain expertise along with in-depth experience of variety of insurance products has been instrumental in bringing quality, innovation, and earning client confidence in the project deliveries. Vikram has done Master in Commerce and is a Fellow from III (Affiliated to CII UK) and a Certificate in General Insurance from Insurance Institute of America.

