Apache Hive is a distributed, fault-tolerant data warehouse system that enables analytics at a massive scale. Like all data warehouses, it provides users with a centralized place to store information for easy analysis and data-driven decision-making. Hive specifically allows users to read, write, and manage petabytes of data using SQL.
Using MuleSoft to connect Hive-DB unlocks connectivity for more systems within an organization’s application network. It also does so faster and more securely than other methods.
This blog explains reading Apache Hive-DB data with MuleSoft Database Connector. It uses Kerberos authentication to authenticate with Hive-DB.
Prerequisites
You’ll need the following prerequisites to complete this process:
- Anypoint Studio 7.0
- MuleSoft Database Connector
- Cloudera JDBC Driver (ClouderaHiveJDBC42-2.6.18.1021)
- The below config files:
- Jaas.conf
- Krb5.conf
- {MulesoftUser}.keytab
Note:
The krb5.conf and MulesoftUser}.keytab files should be provided through the Hadoop/Hive team.
What the krb5.conf file looks like:

Jaas.conf

Note:
Kerberos authentication won’t work if the above “Client” root node is changed or missing.
{MulesoftUser}.keytab
The {MulesoftUser}.keytab file is generated after a service user in AD for Hadoop Hive-DB access is created. This serves as a credential file for the user and is an essential step for authenticating using Kerberos.
Use this command to check principal for the keytab:
klist -t -k MulesoftUser.keytab
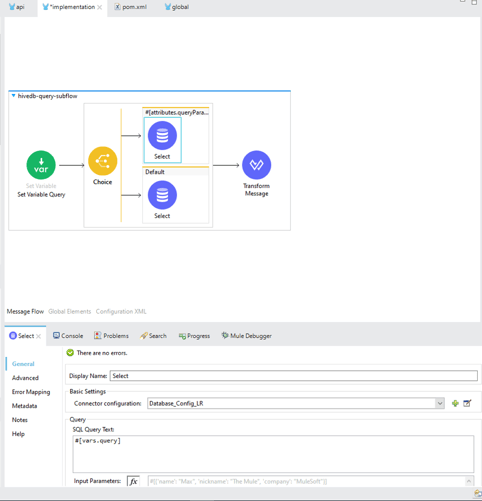
Workflow
The flow presented below is API based and receives database queries from post requests. It directs requests to the appropriate database cluster based on the query parameters, the response for which is then transformed and sent back to the caller.
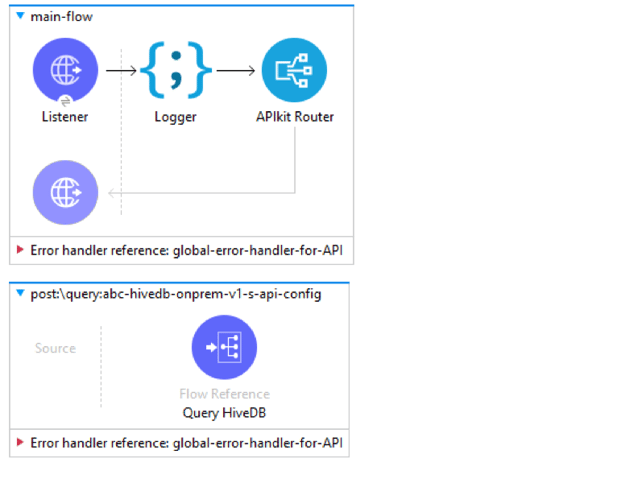
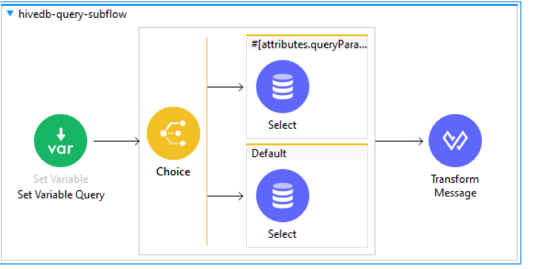
Steps:
1. Download database connector from Mule palette.
2. This will add the following dependency in POM.xml

3. Add the ClouderaHiveJDBC42-2.6.18.1021 driver to your organization repository manager (example: Artifactory/nexus etc.).
Ref: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24122382/how-to-configure-maven2-to-publish-to-artifactory
4. Add ClouderaHiveJDBC42-2.6.18.1021 to the POM dependency and share-library


5. Add the below database configuration in global.xml:
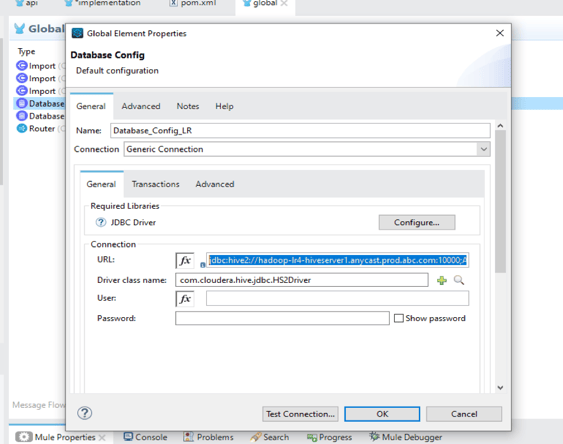
URL pattern:
jdbc:hive2://hadoop-lr4-hiveserver1.anycast.prod.abc.com:10000;AuthMech=1;KrbRealm=ABCDATA.COM;KrbHostFQDN=http://hadoop-lr4-hiveserver1.anycast.prod.abc.com;KrbServiceName=hive;KrbAuthType=1
Note:
Please also add your reconnection strategy at this step.
| hadoop-lr4-hiveserver1.anycast.prod.abc.com |
Host |
| 10000 |
Port |
| AuthMech |
1, means Kerberos authentication |
| ABCDATA.COM |
KrbRealm, the domain over which a Kerberos authentication server has the authority to authenticate a user, host or service |
| http://hadoop-lr4-hiveserver1.anycast.prod.abc.com |
KrbHostFQDN, used to connect to kerberos host with fully qualified domain name. |
| hive |
KrbServiceName |
| 1 |
KrbAuthType, to create a LoginContext from a JAAS configuration and then use the Subject associated with it, set the KrbAuthType property to 1. |
6. Set up your API kit router and bind it with the appropriate sub-flow and database config per the above workflow.
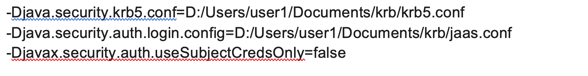
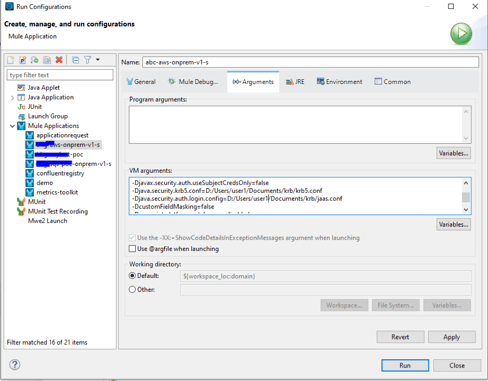
7. Once the flow is completed, add the following properties and run configurations.
Note:
Be sure to provide the appropriate krb5.conf and jaas.conf paths as per the above prerequisites.
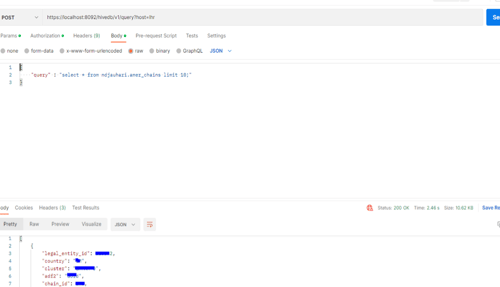
8. Fire a query to your hive-DB using postman.
References:
To find out more email us at: salesforce@coforge.com














