Regional and community banks in the U.S. are facing increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, rising operational costs, and intensifying competition from digital-first financial institutions. Fenergo reports that 80 fines totaling $263,252,003 were imposed by global financial regulators in the first half of 2024 for violations of anti-money laundering (AML) laws, which include sanctions, transaction monitoring infractions, know your customer (KYC) requirements, and suspicious activity reports (SARs).
This underscores the need for banks to proactively identify potential points of failure within their processes and mitigate risks before they become costly liabilities.
In addition to financial penalties, operational inefficiencies and cybersecurity risks have compounded the challenges faced by regional banks. This blog explores the most common points of failure and provides a roadmap to minimizing risk exposure through strategic assessments and technology-driven interventions.
Risk Management: An Absolute Necessity For Banks
Risk management is the backbone of every bank’s survival, but for regional and community banks, the stakes are particularly high. With limited resources compared to larger institutions, even minor operational failures can lead to significant financial losses and damage to reputation. A comprehensive risk management strategy is essential to identify gaps in processes, reduce operational risks, and ensure compliance with evolving regulatory frameworks.
To mitigate risks, regulators now require banks over $50 billion in assets to have a CRO and a board risk committee since the financial crash experienced due to two prominent banks collapsing in March 2023.
Silicon Valley Bank had over $200 billion in assets typically dealing with startups and venture investments. Unfortunately, without any CFO or risk assessment committee to take decisions when their structure collapsed, the bank had to be taken over by regulators and put under a bridge bank. This highlights the importance of risk assessments, stress testing, and internal control evaluations, which help banks pinpoint their vulnerabilities and prepare for potential disruptions.
Identifying Common Points of Failure
To minimize risk exposure, banks must first identify the common points of failure within their operations. These points of failure can be categorized into the following areas:
Compliance and Regulatory Gaps:
Many regional banks struggle to keep up with evolving regulatory requirements such as the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Failure to monitor compliance effectively results in heavy fines and loss of customer trust. For instance, in 2022, banks faced a total of $5.7 billion in AML-related penalties.
Manual Processes and Human Errors:
While manual processes might be manageable for smaller institutions, they introduce significant risks in the form of human error and inefficiency. These errors can lead to incorrect reporting, missed deadlines, and compliance breaches.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities:
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, regional banks remain prime targets for cyberattacks due to limited cybersecurity resources. The CL0P-MOVEit attack impacted nearly 1,000 public and private sector organizations, including various U.S. agencies and large corporations including Deloitte, Ernst & Young, and Deutsche Bank. Unsecured systems, outdated software, and insufficient employee training are common failure points.
Outdated Technology Infrastructure:
Legacy systems often hinder regional banks' ability to compete and remain compliant. Without the ability to update processes or integrate modern technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning, banks risk falling behind in operational efficiency and fraud detection capabilities.
Minimizing Risk Exposure Starts With Process Assessment
Addressing these potential points of failure requires a multifaceted approach involving process improvement, technology adoption, and a strong focus on risk management culture. Below are strategies to minimize risk exposure for regional and community banks:
Process Mapping and Risk Assessment:
Banks should begin by conducting a thorough process mapping exercise to identify inefficiencies and high-risk areas. This can be achieved through tech-led process assessments, which allow banks to observe workflows in real-time, detect bottlenecks, and gain valuable data-driven insights. Such assessments help ensure that critical processes—such as transaction monitoring, customer onboarding, and reporting—are optimized for accuracy and speed.
Leveraging Technology for Risk Mitigation:
Automation tools like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can eliminate manual errors, streamline compliance, and improve overall operational efficiency. Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns in transactions to flag suspicious activities, while AI-powered predictive analytics can foresee operational risks before they escalate.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Defences:
Investing in cybersecurity infrastructure is no longer optional but a necessity. Regional banks should consider multi-layered defence systems, regular vulnerability assessments, and robust employee training programs. Additionally, adopting encryption, secure cloud services, and continuous monitoring systems can help mitigate the risks of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Implementing a Strong Risk Culture:
Risk management should not only be the responsibility of the compliance department but ingrained into the institution’s culture. By establishing a risk-aware culture, banks can ensure that employees at all levels understand the importance of safeguarding customer information, maintaining regulatory compliance, and following standard operating procedures.
However, manual process assessments are time-consuming and require significant effort, involving extensive documentation reviews, stakeholder interviews, and workflow mapping. This can delay necessary improvements and tie up resources that could be used more effectively elsewhere. The high effort involved can lead to fatigue and errors, impacting the quality and accuracy of the assessment.
Cut Down Your Assessment Time with our Tech-led Assessment
Get an accurate assessment of your existing processes with data-backed insights to rebuild your processes and integrate technology solutions to minimize risk with Coforge's proprietary framework ProcessGym and industry-leading tools Cognitio Analytics and SkanAI.
A typical process assessment has the following workflow
 VS
VS
Coforge Tech-led Assessment
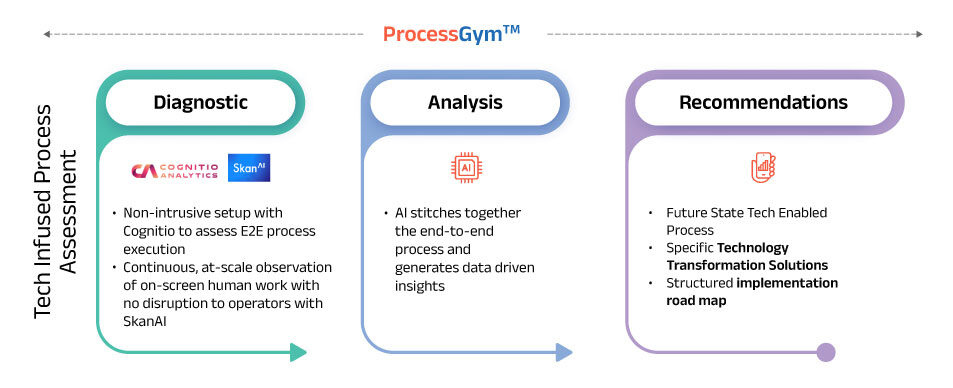 In order to minimize the risk exposure to banks, lower operating expenses, and improve customer happiness, our domain experts and six-sigma practitioners offer collaboration at every stage of the process redesigning.
In order to minimize the risk exposure to banks, lower operating expenses, and improve customer happiness, our domain experts and six-sigma practitioners offer collaboration at every stage of the process redesigning.
Conclusion
Regional and community banks face unique challenges when it comes to risk management, but by proactively identifying potential points of failure, they can minimize risk exposure, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with evolving regulations. Adopting advanced technologies like AI, RPA, and cybersecurity tools will not only mitigate risks but also enhance the customer experience and strengthen the bank’s overall performance.
Investing in process assessments and risk mitigation strategies today will protect regional banks from costly errors tomorrow. By understanding where their vulnerabilities lie and addressing them, banks can remain competitive, secure, and compliant in an increasingly complex financial landscape.
Discover Mayur Gangwani's expertise on Coforge's blog. Learn about digital transformation and enterprise solutions.
Related reads.

About Coforge.
We are a global digital services and solutions provider, who leverage emerging technologies and deep domain expertise to deliver real-world business impact for our clients. A focus on very select industries, a detailed understanding of the underlying processes of those industries, and partnerships with leading platforms provide us with a distinct perspective. We lead with our product engineering approach and leverage Cloud, Data, Integration, and Automation technologies to transform client businesses into intelligent, high-growth enterprises. Our proprietary platforms power critical business processes across our core verticals. We are located in 23 countries with 30 delivery centers across nine countries.



